M2.5 natively supports Interleaved Thinking, enabling it to reason between each round of tool interactions. Before every Tool Use, the model reflects on the current environment and the tool outputs to decide its next action.
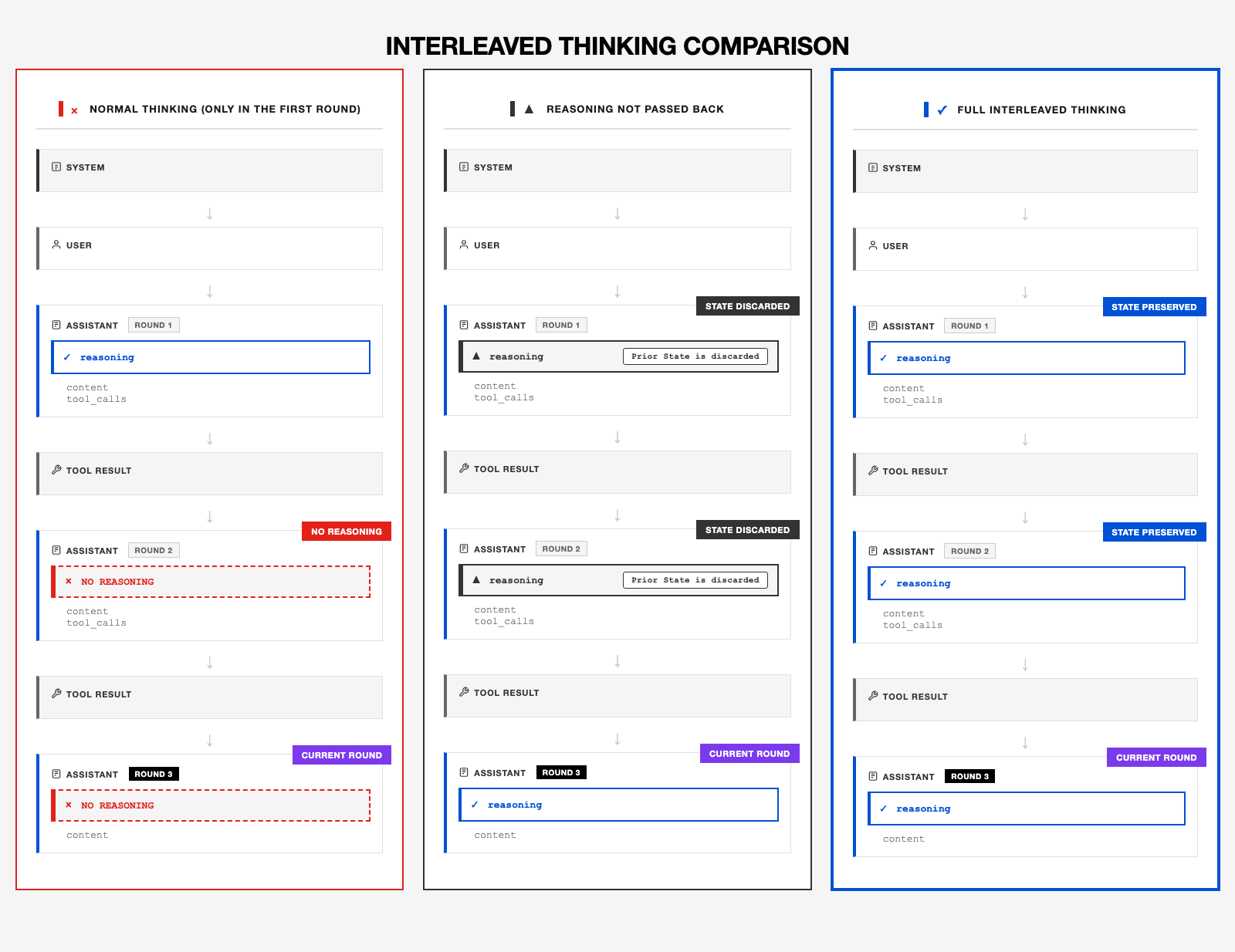 This ability allows M2.5 to excel at long-horizon and complex tasks, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on benchmarks such as SWE, BrowseCamp, and xBench, which test both coding and agentic reasoning performance.
In the following examples, we’ll illustrate best practices for Tool Use and Interleaved Thinking with M2.5. The key principle is to return the model’s full response each time—especially the internal reasoning fields (e.g., thinking or reasoning_details).
This ability allows M2.5 to excel at long-horizon and complex tasks, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on benchmarks such as SWE, BrowseCamp, and xBench, which test both coding and agentic reasoning performance.
In the following examples, we’ll illustrate best practices for Tool Use and Interleaved Thinking with M2.5. The key principle is to return the model’s full response each time—especially the internal reasoning fields (e.g., thinking or reasoning_details).
Parameters
Request Parameters
tools: Defines the list of callable functions, including function names, descriptions, and parameter schemas
Response Parameters
Key fields in Tool Use responses:
thinking/reasoning_details: The model’s thinking/reasoning processtext/content: The text content output by the modeltool_calls: Contains information about functions the model has decided to invokefunction.name: The name of the function being calledfunction.arguments: Function call parameters (JSON string format)id: Unique identifier for the tool call
Important Note
In multi-turn function call conversations, the complete model response (i.e., the assistant message) must be append to the conversation history to maintain the continuity of the reasoning chain.
OpenAI SDK:
- Append the full
response_message object (including the tool_calls field) to the message history
- When using MiniMax-M2.5, the
content field contains <think> tags which will be automatically preserved
- In the Interleaved Thinking Compatible Format, by using the additional parameter (
reasoning_split=True), the model’s thinking content is separated into the reasoning_details field. This content also needs to be added to historical messages.
Anthropic SDK:
- Append the full
response.content list to the message history (includes all content blocks: thinking/text/tool_use)
See examples below for implementation details.
Examples
Anthropic SDK
For international users, use https://api.minimax.io/anthropic; for users in China, use https://api.minimaxi.com/anthropic
export ANTHROPIC_BASE_URL=https://api.minimax.io/anthropic
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=${YOUR_API_KEY}
Example
import anthropic
import json
# Initialize client
client = anthropic.Anthropic()
# Define tool: weather query
tools = [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get weather of a location, the user should supply a location first.",
"input_schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, US",
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
]
def send_messages(messages):
params = {
"model": "MiniMax-M2.5",
"max_tokens": 4096,
"messages": messages,
"tools": tools,
}
response = client.messages.create(**params)
return response
def process_response(response):
thinking_blocks = []
text_blocks = []
tool_use_blocks = []
# Iterate through all content blocks
for block in response.content:
if block.type == "thinking":
thinking_blocks.append(block)
print(f"💭 Thinking>\n{block.thinking}\n")
elif block.type == "text":
text_blocks.append(block)
print(f"💬 Model>\t{block.text}")
elif block.type == "tool_use":
tool_use_blocks.append(block)
print(f"🔧 Tool>\t{block.name}({json.dumps(block.input, ensure_ascii=False)})")
return thinking_blocks, text_blocks, tool_use_blocks
# 1. User query
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "How's the weather in San Francisco?"}]
print(f"\n👤 User>\t {messages[0]['content']}")
# 2. Model returns first response (may include tool calls)
response = send_messages(messages)
thinking_blocks, text_blocks, tool_use_blocks = process_response(response)
# 3. If tool calls exist, execute tools and continue conversation
if tool_use_blocks:
# ⚠️ Critical: Append the assistant's complete response to message history
# response.content contains a list of all blocks: [thinking block, text block, tool_use block]
# Must be fully preserved, otherwise subsequent conversation will lose context
messages.append({
"role": "assistant",
"content": response.content
})
# Execute tool and return result (simulating weather API call)
print(f"\n🔨 Executing tool: {tool_use_blocks[0].name}")
tool_result = "24℃, sunny"
print(f"📊 Tool result: {tool_result}")
# Add tool execution result
messages.append({
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "tool_result",
"tool_use_id": tool_use_blocks[0].id,
"content": tool_result
}
]
})
# 4. Get final response
final_response = send_messages(messages)
process_response(final_response)
👤 User> How's the weather in San Francisco?
💭 Thinking>
Okay, so the user is asking about the weather in San Francisco. This is a straightforward request that requires me to get current weather information for a specific location.
Looking at my available tools, I see I have a `get_weather` function that can provide weather information for a location. This is exactly what I need to answer the user's question. The function requires a "location" parameter, which should be a string containing the city and potentially the state/country.
In this case, the user has clearly specified San Francisco as the location. San Francisco is a major city in US, so I don't need to include the country code - just "San Francisco" should be sufficient for the weather service to identify the correct location.
The required parameters for the get_weather tool are:
- location: "San Francisco"
I should call this tool to retrieve the current weather information for San Francisco before I can provide a meaningful answer to the user. Once I get the weather data back from the tool, I'll be able to share details like temperature, conditions (sunny, cloudy, rainy, etc.), and possibly other relevant information like humidity or wind speed.
So I'll make a tool call to get_weather with the location parameter set to "San Francisco". After I receive the response from this tool call, I'll be able to provide the user with the current weather information they requested.
🔧 Tool> get_weather({"location": "San Francisco"})
🔨 Executing tool: get_weather
📊 Tool result: 24℃, sunny
💭 Thinking>
I've just called the get_weather tool to check the current conditions in San Francisco as the user requested. Let me analyze what information I received back.
The tool returned a simple response: "24℃, sunny". This is quite straightforward - it tells me the current temperature is 24 degrees Celsius and the weather conditions are sunny. This is exactly the basic weather information the user was asking about.
The temperature is given in Celsius (24℃), which is appropriate since US uses the metric system. I could convert this to Fahrenheit for users who might be more familiar with that scale, but since the user didn't specify a preference, I'll stick with the metric measurement as provided by the tool.
For the weather condition, I received "sunny" which indicates clear skies and good visibility. This is useful information that tells the user they can expect good weather if they're planning to be outside.
I don't have additional details like humidity, wind speed, or UV index from the tool response. If the user wants more detailed information, they could ask a follow-up question, and I might need to provide general advice about sunny weather conditions or suggest checking a more detailed weather service.
Now I need to formulate a clear, concise response to the user that directly answers their question about the weather in San Francisco. I'll keep it simple and factual, stating the temperature and conditions clearly. I should also add a friendly closing to invite further questions if needed.
The most straightforward way to present this information is to state the temperature first, followed by the conditions, and then add a friendly note inviting the user to ask for more information if they want it.
💬 Model> The current weather in San Francisco is 24℃ and sunny.
{
"id": "05566b15ee32962663694a2772193ac7",
"type": "message",
"role": "assistant",
"model": "MiniMax-M2.5",
"content": [
{
"thinking": "Let me think about this request. The user is asking about the weather in San Francisco. This is a straightforward request that requires current weather information.\n\nTo provide accurate weather information, I need to use the appropriate tool. Looking at the tools available to me, I see there's a \"get_weather\" tool that seems perfect for this task. This tool requires a location parameter, which should include both the city and state/region.\n\nThe user has specified \"San Francisco\" as the location, but they haven't included the state. For the US, it's common practice to include the state when specifying a city, especially for well-known cities like San Francisco that exist in multiple states (though there's really only one San Francisco that's famous).\n\nAccording to the tool description, I need to provide the location in the format \"San Francisco, US\" - with the city, comma, and the country code for the United States. This follows the standard format specified in the tool's parameter description: \"The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, US\".\n\nSo I need to call the get_weather tool with the location parameter set to \"San Francisco, US\". This will retrieve the current weather information for San Francisco, which I can then share with the user.\n\nI'll format my response using the required XML tags for tool calls, providing the tool name \"get_weather\" and the arguments as a JSON object with the location parameter set to \"San Francisco, US\".",
"signature": "cfa12f9d651953943c7a33278051b61f586e2eae016258ad6b824836778406bd",
"type": "thinking"
},
{
"type": "tool_use",
"id": "call_function_3679004591_1",
"name": "get_weather",
"input": {
"location": "San Francisco, US"
}
}
],
"usage": {
"input_tokens": 222,
"output_tokens": 321
},
"stop_reason": "tool_use",
"base_resp": {
"status_code": 0,
"status_msg": ""
}
}
OpenAI SDK
For international users, use https://api.minimax.io/v1; for users in China, use https://api.minimaxi.com/v1
export OPENAI_BASE_URL=https://api.minimax.io/v1
export OPENAI_API_KEY=${YOUR_API_KEY}
reasoning_split=True to get a more developer-friendly output format.
Important Note: To ensure that Interleaved Thinking functions properly and the model’s chain of thought remains uninterrupted, the entire response_message — including the reasoning_details field — must be preserved in the message history and passed back to the model in the next round of interaction.This is essential for achieving the model’s best performance.
send_messages) is implemented, as well as how you append the historical messages with messages.append(response_message).
import json
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
# Define tool: weather query
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get weather of a location, the user should supply a location first.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, US",
}
},
"required": ["location"],
},
},
},
]
def send_messages(messages):
"""Send messages and return response"""
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="MiniMax-M2.5",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
# Set reasoning_split=True to separate thinking content into reasoning_details field
extra_body={"reasoning_split": True},
)
return response.choices[0].message
# 1. User query
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "How's the weather in San Francisco?"}]
print(f"👤 User>\t {messages[0]['content']}")
# 2. Model returns tool call
response_message = send_messages(messages)
if response_message.tool_calls:
tool_call = response_message.tool_calls[0]
function_args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
print(f"💭 Thinking>\t {response_message.reasoning_details[0]['text']}")
print(f"💬 Model>\t {response_message.content}")
print(f"🔧 Tool>\t {tool_call.function.name}({function_args['location']})")
# 3. Execute tool and return result
messages.append(response_message)
messages.append(
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": "24℃, sunny", # In real applications, call actual weather API here
}
)
# 4. Get final response
final_message = send_messages(messages)
print(
f"💭 Thinking>\t {final_message.model_dump()['reasoning_details'][0]['text']}"
)
print(f"💬 Model>\t {final_message.content}")
else:
print(f"💬 Model>\t {response_message.content}")
👤 User> How's the weather in San Francisco?
💭 Thinking> Alright, the user is asking about the weather in San Francisco. This is a straightforward question that requires real-time information about current weather conditions.
Looking at the available tools, I see I have access to a "get_weather" tool that's specifically designed for this purpose. The tool requires a "location" parameter, which should be in the format of city and state, like "San Francisco, CA".
The user has clearly specified they want weather information for "San Francisco" in their question. However, they didn't include the state (California), which is recommended for the tool parameter. While "San Francisco" alone might be sufficient since it's a well-known city, for accuracy and to follow the parameter format, I should include the state as well.
Since I need to use the tool to get the current weather information, I'll need to call the "get_weather" tool with "San Francisco, CA" as the location parameter. This will provide the user with the most accurate and up-to-date weather information for their query.
I'll format my response using the required tool_calls XML tags and include the tool name and arguments in the specified JSON format.
💬 Model>
🔧 Tool> get_weather(San Francisco, US)
💭 Thinking> Okay, I've received the user's question about the weather in San Francisco, and I've used the get_weather tool to retrieve the current conditions.
The tool has returned a simple response: "24℃, sunny". This gives me two pieces of information - the temperature is 24 degrees Celsius, and the weather condition is sunny. That's quite straightforward and matches what I would expect for San Francisco on a nice day.
Now I need to present this information to the user in a clear, concise way. Since the response from the tool was quite brief, I'll keep my answer similarly concise. I'll directly state the temperature and weather condition that the tool provided.
I should make sure to mention that this information is current, so the user understands they're getting up-to-date conditions. I don't need to provide additional details like humidity, wind speed, or forecast since the user only asked about the current weather.
The temperature is given in Celsius (24℃), which is the standard metric unit, so I'll leave it as is rather than converting to Fahrenheit, though I could mention the conversion if the user seems to be more familiar with Fahrenheit.
Since this is a simple informational query, I don't need to ask follow-up questions or suggest activities based on the weather. I'll just provide the requested information clearly and directly.
My response will be a single sentence stating the current temperature and weather conditions in San Francisco, which directly answers the user's question.
💬 Model> The weather in San Francisco is currently sunny with a temperature of 24℃.
{
"id": "05566b8d51ded3a3016d6cc100685cad",
"choices": [
{
"finish_reason": "tool_calls",
"index": 0,
"message": {
"content": "\n",
"role": "assistant",
"name": "MiniMax AI",
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_function_2831178524_1",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\": \"San Francisco, US\"}"
},
"index": 0
}
],
"audio_content": "",
"reasoning_details": [
{
"type": "reasoning.text",
"id": "reasoning-text-1",
"format": "MiniMax-response-v1",
"index": 0,
"text": "Let me think about this request. The user is asking about the weather in San Francisco. This is a straightforward request where they want to know current weather conditions in a specific location.\n\nLooking at the tools available to me, I have access to a \"get_weather\" tool that can retrieve weather information for a location. The tool requires a location parameter in the format of \"city, state\" or \"city, country\". In this case, the user has specified \"San Francisco\" which is a city in the United States.\n\nTo properly use the tool, I need to format the location parameter correctly. The tool description mentions examples like \"San Francisco, US\" which follows the format of city, country code. However, since the user just mentioned \"San Francisco\" without specifying the state, and San Francisco is a well-known city that is specifically in California, I could use \"San Francisco, CA\" as the parameter value instead.\n\nActually, \"San Francisco, US\" would also work since the user is asking about the famous San Francisco in the United States, and there aren't other well-known cities with the same name that would cause confusion. The US country code is explicit and clear.\n\nBoth \"San Francisco, CA\" and \"San Francisco, US\" would be valid inputs for the tool. I'll go with \"San Francisco, US\" since it follows the exact format shown in the tool description example and is unambiguous.\n\nSo I'll need to call the get_weather tool with the location parameter set to \"San Francisco, US\". This will retrieve the current weather information for San Francisco, which I can then present to the user."
}
]
}
}
],
"created": 1762080909,
"model": "MiniMax-M2.5",
"object": "chat.completion",
"usage": {
"total_tokens": 560,
"total_characters": 0,
"prompt_tokens": 203,
"completion_tokens": 357
},
"input_sensitive": false,
"output_sensitive": false,
"input_sensitive_type": 0,
"output_sensitive_type": 0,
"output_sensitive_int": 0,
"base_resp": {
"status_code": 0,
"status_msg": ""
}
}
content field in the form of <think>reasoning_content</think>. Developers can manually parse it for display purposes. However, we strongly recommend developers use the Interleaved Thinking compatible format.
What extra_body={"reasoning_split": False} does:
- Embeds thinking in content: The model’s reasoning is wrapped in
<think> tags within the content field
- Requires manual parsing: You need to parse
<think> tags if you want to display reasoning separately
Important Reminder: If you choose to use the native format, please note that in the message history, do not modify the content field. You must preserve the model’s thinking content completely, i.e., <think>reasoning_content</think>. This is essential to ensure Interleaved Thinking works effectively and achieves optimal model performance!
from openai import OpenAI
import json
# Initialize client
client = OpenAI(
api_key="<api-key>",
base_url="https://api.minimax.io/v1",
)
# Define tool: weather query
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get weather of a location, the user should supply a location first.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, US",
}
},
"required": ["location"]
},
}
},
]
def send_messages(messages):
"""Send messages and return response"""
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="MiniMax-M2.5",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
# Set reasoning_split=False to keep thinking content in <think> tags within content field
extra_body={"reasoning_split": False},
)
return response.choices[0].message
# 1. User query
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "How's the weather in San Francisco?"}]
print(f"👤 User>\t {messages[0]['content']}")
# 2. Model returns tool call
response_message = send_messages(messages)
if response_message.tool_calls:
tool_call = response_message.tool_calls[0]
function_args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
print(f"💬 Model>\t {response_message.content}")
print(f"🔧 Tool>\t {tool_call.function.name}({function_args['location']})")
# 3. Execute tool and return result
messages.append(response_message)
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": "24℃, sunny" # In production, call actual weather API here
})
# 4. Get final response
final_message = send_messages(messages)
print(f"💬 Model>\t {final_message.content}")
else:
print(f"💬 Model>\t {response_message.content}")
👤 User> How's the weather in San Francisco?
💬 Model> <think>
Alright, the user is asking about the weather in San Francisco. This is a straightforward request that I can handle using the tools provided to me.
I see that I have access to a tool called "get_weather" which can provide weather information for a location. Looking at the parameters, it requires a "location" parameter which should be a string in the format of "city and state, e.g. San Francisco, US".
In this case, the user has already specified the location as "San Francisco", which is a major city in California, US. I need to format this properly for the tool call. Following the example format in the tool description, I should format it as "San Francisco, US".
The user didn't specify any other parameters or requirements, so a simple weather query should be sufficient. I don't need to ask for clarification since they've provided a clear location.
Let me prepare the tool call to get the weather information for San Francisco. I'll use the "get_weather" tool with the location parameter set to "San Francisco, US". This should return the current weather conditions for San Francisco, which is what the user is asking about.
Once I get the weather information back from the tool, I'll be able to provide the user with details about the current weather in San Francisco, such as temperature, conditions (sunny, cloudy, rainy, etc.), and possibly other relevant information like humidity or wind speed if that data is available.
So I'll proceed with making the tool call to get_weather with the location parameter.
</think>
🔧 Tool> get_weather(San Francisco, US)
💬 Model> <think>
Let me analyze what's happening in this conversation. The user asked about the weather in San Francisco, and I needed to provide them with this information.
Looking at the tools available to me, I have access to a "get_weather" tool that can retrieve weather information for a specific location. I used this tool and called it with the argument "location": "San Francisco, US" as specified in the tool's parameters.
The tool has now returned a response with the weather information for San Francisco. The response is quite concise - it simply states "24℃, sunny". This gives me two pieces of information:
1. The temperature is 24 degrees Celsius
2. The weather condition is sunny
This is exactly what the user wanted to know - how's the weather in San Francisco. The information is clear and straightforward.
Now I need to format this information in a clear, natural way for the user. Since the tool returned the temperature in Celsius, I'll use that unit rather than converting to Fahrenheit (though 24°C is about 75°F if the user happens to think in those terms).
I should keep my response concise since the weather information itself is simple. I don't need to add any caveats or additional explanations since the weather report is straightforward. I won't include any details about wind, humidity, or other meteorological data since the tool didn't provide that information.
So my response will simply state the current temperature and that it's sunny in San Francisco, which directly answers the user's question.
</think>
The weather in San Francisco is currently sunny with a temperature of 24℃.
{
"id": "055b7928a143b2d21ad6b2bab2c8f8b2",
"choices": [{
"finish_reason": "tool_calls",
"index": 0,
"message": {
"content": "<think>\nAlright, the user is asking about the weather in San Francisco. This is a straightforward request that I can handle using the tools provided to me.\n\nI see that I have access to a tool called \"get_weather\" which can provide weather information for a location. Looking at the parameters, it requires a \"location\" parameter which should be a string in the format of \"city and state, e.g. San Francisco, US\".\n\nIn this case, the user has already specified the location as \"San Francisco\", which is a major city in California, US. I need to format this properly for the tool call. Following the example format in the tool description, I should format it as \"San Francisco, US\".\n\nThe user didn't specify any other parameters or requirements, so a simple weather query should be sufficient. I don't need to ask for clarification since they've provided a clear location.\n\nLet me prepare the tool call to get the weather information for San Francisco. I'll use the \"get_weather\" tool with the location parameter set to \"San Francisco, US\". This should return the current weather conditions for San Francisco, which is what the user is asking about.\n\nOnce I get the weather information back from the tool, I'll be able to provide the user with details about the current weather in San Francisco, such as temperature, conditions (sunny, cloudy, rainy, etc.), and possibly other relevant information like humidity or wind speed if that data is available.\n\nSo I'll proceed with making the tool call to get_weather with the location parameter.\n</think>\n\n\n",
"role": "assistant",
"name": "MiniMax AI",
"tool_calls": [{
"id": "call_function_1202729600_1",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\": \"San Francisco, US\"}"
},
"index": 0
}],
"audio_content": ""
}
}],
"created": 1762412072,
"model": "MiniMax-M2.5",
"object": "chat.completion",
"usage": {
"total_tokens": 560,
"total_characters": 0,
"prompt_tokens": 222,
"completion_tokens": 338
},
"input_sensitive": false,
"output_sensitive": false,
"input_sensitive_type": 0,
"output_sensitive_type": 0,
"output_sensitive_int": 0,
"base_resp": {
"status_code": 0,
"status_msg": ""
}
}
Recommended Reading
 This ability allows M2.5 to excel at long-horizon and complex tasks, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on benchmarks such as SWE, BrowseCamp, and xBench, which test both coding and agentic reasoning performance.
In the following examples, we’ll illustrate best practices for Tool Use and Interleaved Thinking with M2.5. The key principle is to return the model’s full response each time—especially the internal reasoning fields (e.g., thinking or reasoning_details).
This ability allows M2.5 to excel at long-horizon and complex tasks, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on benchmarks such as SWE, BrowseCamp, and xBench, which test both coding and agentic reasoning performance.
In the following examples, we’ll illustrate best practices for Tool Use and Interleaved Thinking with M2.5. The key principle is to return the model’s full response each time—especially the internal reasoning fields (e.g., thinking or reasoning_details).